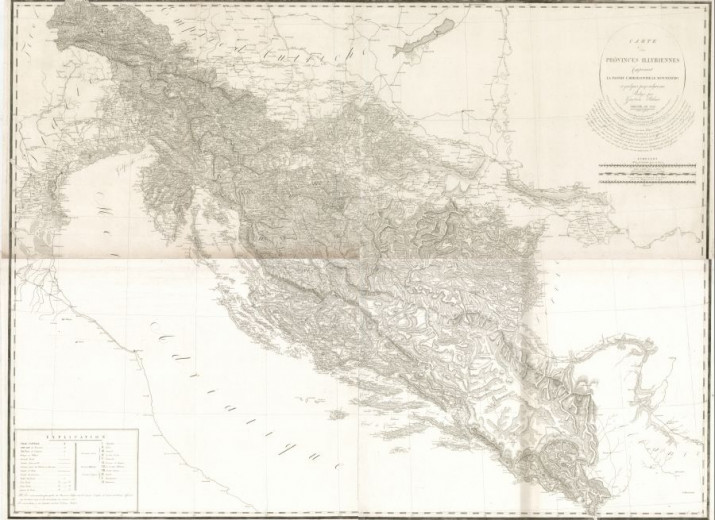
1 January–30 June 2008: Slovenian Presidency of the Council of the EU.
1 January 2007: Slovenia introduces the euro.
1 May 2004: Slovenia becomes a member of the EU.
29 March 2004: Slovenia becomes a member of NATO.
1 February 1999: The association agreement with the EU enters into force.
22 May 1992: Slovenia becomes a permanent member of the UN.
15 January 1992: The EU officially recognises Slovenia.
25 June 1991: Declaration of the independent Republic of Slovenia.
23 December 1991: Adoption of the new Slovenian Constitution.
1990: Plebiscite on independence.
-

Plebiscite poster, 1990. Photo: National Museum of Contemporary History of Slovenia archives
-
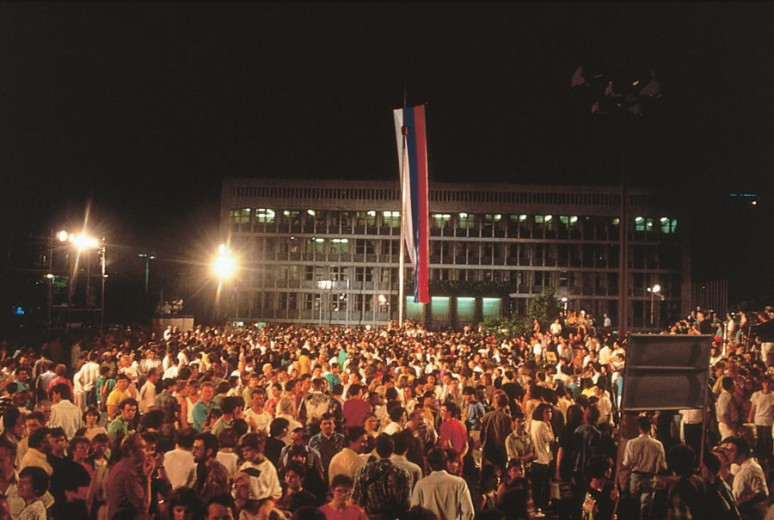

Declaration of independence. Photo: Srđan Živulovič/BOBO
-
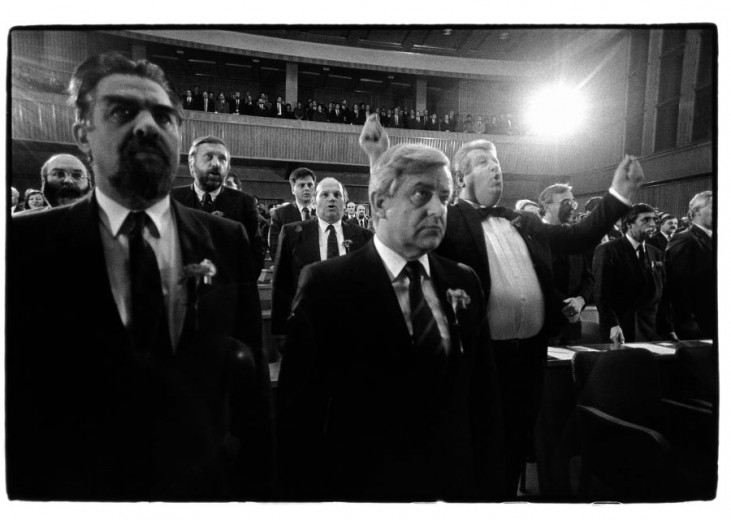

President of the Republic of Slovenia Milan Kučan, 1990, in the Parliament. Photo: National Museum of Contemporary History of Slovenia archives
-

In the front of the Parliament, 1990. Photo: National Museum of Contemporary History of Slovenia archives
-
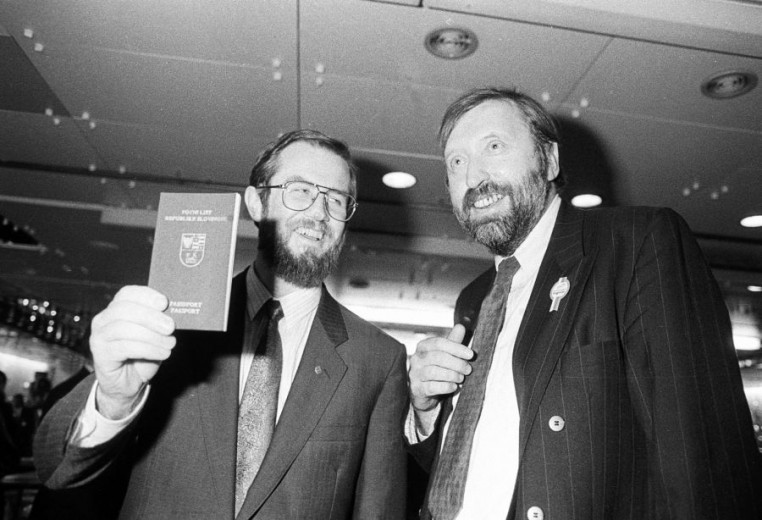

The first passport of the Republic of Slovenia was issued in 1991. It was designed by Miljenko Licul, the father of the Slovenian tolar and the Slovenian euro coins, as well as of Slovenian ID cards and health insurance cards. Photo: National Museum of Contemporary History of Slovenia archives
1945: The formation of the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, with the People's Republic of Slovenia as one of its six federal entities.
1941–1945: The dismemberment of Yugoslavia by the Axis Powers.
1918: The defeat of the Austro-Hungarian Empire; the creation of the state of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs; the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929.
1848: Unified Slovenia, the first Slovenian political programme.
1809–1813: Napoleonic occupation – the Illyrian Provinces.
18th century: The Enlightenment and compulsory universal education.
1550: Protestantism; the first book in the Slovenian language.
15th to 17th centuries: Peasant revolts.
15th century: Turkish invasions begin.
14th to 15th centuries: Most of the territory of Slovenia, including all its hereditary estates, is taken over by the Habsburgs; in 1456, the Counts of Celje, the last feudal dynasty in Slovenia, die out.
11th to 14th centuries: The development of medieval towns in Slovenia.
11th century: The regions of Carniola, Styria, Carinthia and Gorizia begin to develop; intensive German colonisation.
10th century: The appearance of the Freising Manuscripts, the earliest known text written in Slovenian.
9th century: The spread of the Frankish feudal system; the Slovenian nation begins to form.
8th century: The beginnings of the conversion to Christianity.
7th to 11th century: The State of Carantania, the oldest known independent
Slavonic tribal union in this region.
After 568: Dominance of Slavic people on the territory of Slovenia.
5th and 6th century CE: Invasions by the Huns and Germanic tribes.
Around 10 BCE: The Roman Empire; the appearance of the first towns.
4th and 3rd century BCE: The arrival of Celts; the Noricum Kingdom.
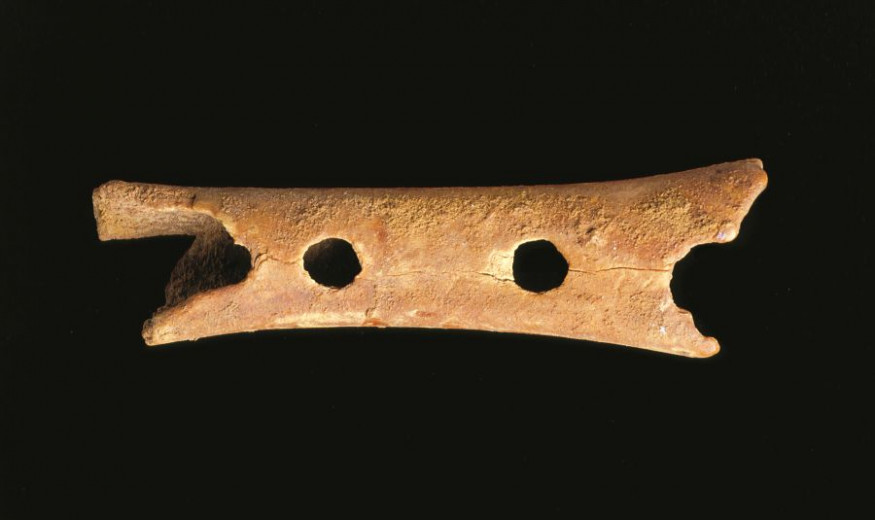
120,000 to 1,300 BCE: Remains from the early Stone Age – the Palaeolithic; among them the oldest musical instrument in the world; evidence of hunting and Urnfield culture.
250,000 BCE: The first evidence of human habitation on the territory of present-day Slovenia (two tools made of stone from Jama Cave in the Loza Woods near Orehek).
Date: 21. October 2019
Time to read: 1 min